While visiting a winery in the Beaujolais district of France a few weeks ago I was introduced to a new term. I was told that the winery I was visiting was a biodynamic winery. This was a description I had not heard before, so I decided to research the topic in more depth when I returned home from my trip.
You may be familiar with what organic farming entails (if not, see my post Organic Wine from August 8, 2020), however the biodynamic movement is somewhat different. According to the Biodynamic Farming and Gardening Association, biodynamics is “a spiritual-ethical-ecological approach to agriculture, gardens, food production and nutrition.” Biodynamic wine is made with a set of farming practices that views the vineyard as one solid organism. The ecosystem functions with each portion of the vineyard contributing to the next. Conceptually, everything in the universe is interconnected and gives off a resonance or ‘vibe’. This interconnectivity even includes celestial bodies like the moon, planets and stars. Biodynamic viticulture is the practice of balancing this resonance between vine, human, earth and stars. Biodynamics is a holistic view of agriculture.
As with organic farming, natural materials, soils, and composts are used to sustain the vineyard. Chemical fertilizers and pesticides are not permitted. A range of animals from ducks to horses to sheep live on the soil and fertilize it, creating a rich, fertile environment for the vines to grow in. Biodynamic farming also seeks sustainability, leaving the land in as good or better condition.
Biodynamic farming has been met with skepticism by many scientists as some of the practices are difficult at best to prove they work. In addition to organic practices, biodynamic farming takes other factors into account, such as the lunar calendar and astrology. This method of farming considers all aspects of life in the vineyard — other plants, insects and animals. It’s not just about the grapes.
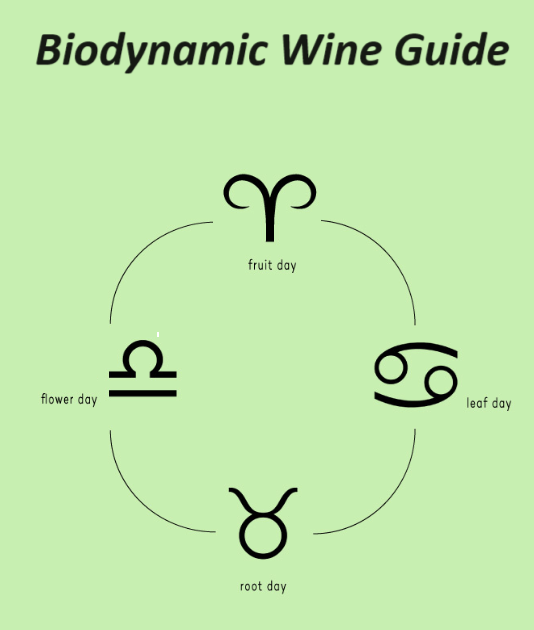
Farming practices from pruning to harvesting are controlled by the biodynamic calendar. It breaks all the tasks associated with farming into four types of days: root days, flower days, fruit days and leaf days. Each of these categories has certain tasks associated with it that are reflective of the earth’s four classical elements. Fruit days are meant for harvesting, leaf days for watering, root days for pruning. On flower days, nothing is done in the vineyard.
Biodynamic farming calls for specific and sometimes strange compost and field preparations. One of these is known as cow horn manure. Cow horns are stuffed with manure compost and buried into the ground all through the winter, then excavated the following spring. When excavated, the stuffed material is spread throughout the vineyard.
Biodynamic wines must be certified and adhere to strict rules and regulations. The wineries are overseen by 2 governing bodies, Demeter International and Biodyvin.
Biodynamic wines can be found in the United States, France, Germany, Spain, Italy, Eastern Europe, Chile, Argentina, India and Australia. Those who believe in the philosophy feel that the wines are more characteristic to the terroir where they originate. However, wine experts say there is no noticeable difference in the taste of biodynamic wine from organically produced wines. Is the difference worth the additional effort? You be the judge.
Sláinte mhaith